First C Program
First C Program
C Programming Tutorial
- C Programming Tutorial
- Features Of C Language
- How to install C Compiler
- First C Program
- How to Run C Program
- Data Type in C Programming Language
- Variables in C Programming Language
- Keywords in C Programming Language
- Constants in C Programming Language
- Operators in C Programming Language
- Conditions Statement In C Programming
First C Program
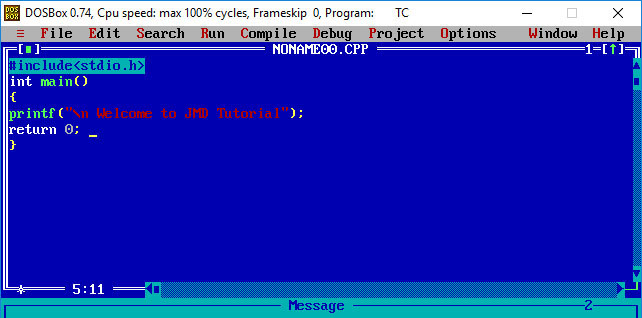
#include < stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf(“\n Hello, JMD Tutorial\n”);
return 0;
}

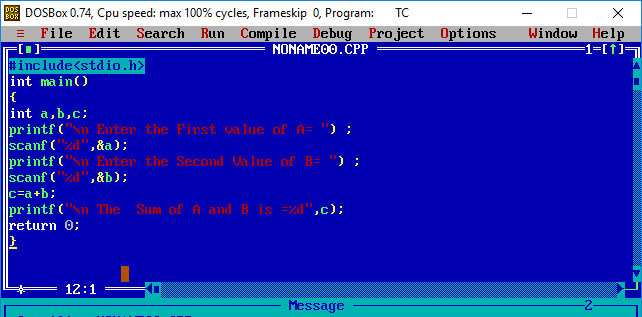
#include < stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a, b,c;
printf(“\n Enter the First value of A=”);
scanf(“%d”, &a);
printf(“\n Ehter the First value of B=”);
scanf(“%d”, &b);
c=a+b;
printf(“\n The sum of A and B is=%d”,c);
return 0;
}

Different parts of C program
Pre-processor
Header file
Function
Variables
Statements & expressions
Comments
In C programming language, #include is the preprocessor. It is also known as a pre-processo. When we try to compile a program, preprocessor commands are first executed and then the program gets compiled.
when we write #include < stdio.h>, it is to inform the compiler to include the stdio.h header file to the program before executing it.
A Header file is a collection of built-in functions. A header file is a file with extension .h. Header files contain definitions of the functions which can be incorporated into any C program by using pre-processor #include statement with the header file.
Every C program must contain a main() function. Everything inside main() function in a C program will be executed.
int written before the main() function is the return type of main() function
In c programming , a variable is a container or storage area to hold data.
int a, b,c; in this declaration anc is variable. we will discuss about variable in detail later.
An expression statement is a particular kind of statement. It consists of an optional expression followed by a semicolon.
x = 42; // the expression happens to be an assignment
Comments in C language are used to provide information about lines of code. It is widely used for documenting code. These comments are ignored by the compiler and are not executed. To add a single line comment, start it by adding two forward slashses // followed by the comment. To add multiline comment, enclode it between /* …. */, just like in the program above.
